The primary function of the measuring instruments is to indicate the accurate values from the measurements. When the force of 100N is applied, the gauge must show the correct measurement results.
All new measuring instruments manufactured are calibrated before shipment to display accurate readings. However, the results may change over time with the environment or the frequency of use. The periodical calibration of the measuring instruments is essential to indicate the correct values. In this article, we explain calibration, which is essential for measuring and obtaining accurate results, and we wish to clarify some of the inquiries.
- What is the force gauge calibration?
- Why is the calibration necessary? What happens when the calibration is not performed?
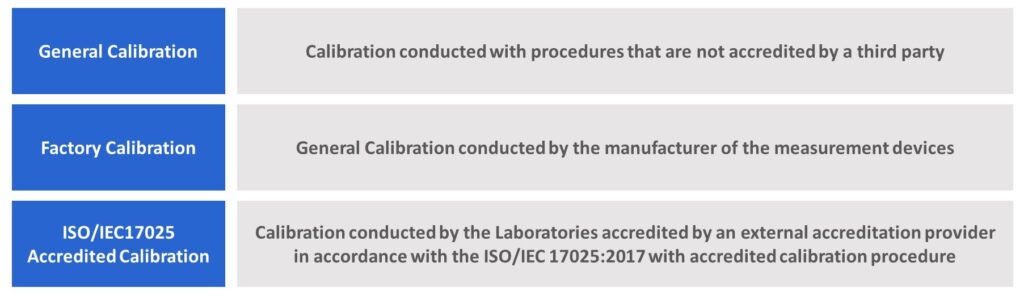
- What are the differences? General Calibration, Factory Calibration, and ISO/IEC17025 Accredited Calibration?
- Which document is needed for the requirements?

What is Calibration of Force Measuring Instruments?
Calibration of force measuring instruments is the process of confirming the value indicated by applying force using calibration standards. By comparing the indicated value with the nominal value of the standard instruments, the accuracy can be confirmed.
For example, if 50N is applied to a force gauge using a calibration weight and the result is 50.08N, the difference is +0.08N. Whether the accuracy of the force gauge is within tolerance can be determined by conducting similar confirmation processes at several points. *1
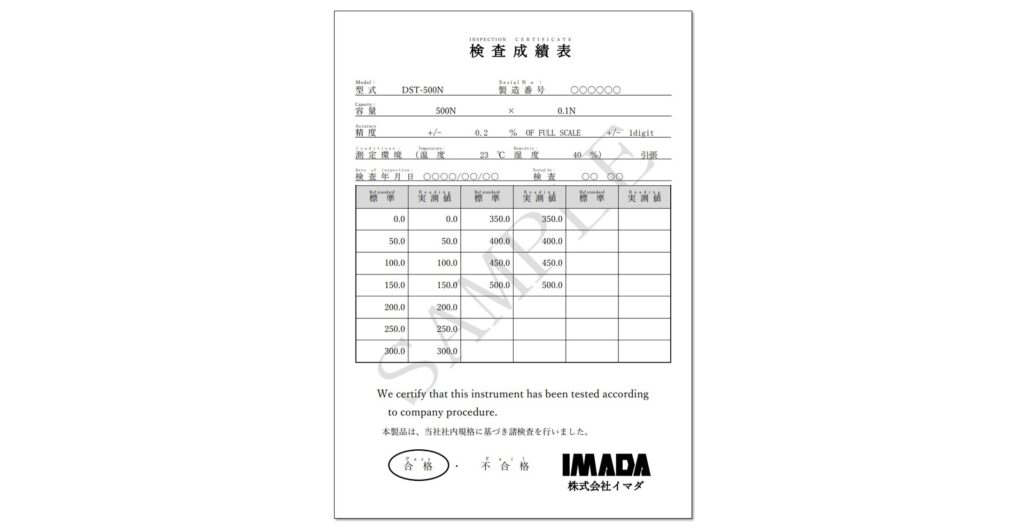
The primary function of the force gauge is to display accurate measurement values, and calibration confirms the reliability of the performance.
A yearly calibration is generally recommended for performance maintenance and to protect product quality standards. When value discrepancies are identified during the calibration, the user needs to investigate the period in which this occurred and the related effects. Before the calibration results fall outside your company standard, proper device maintenance and repairment is highly recommended.
Please note that calibration procedures generally do not include the value adjustment of the measuring instruments. Therefore, if the calibration results are not within the range required by the Standard, the value adjustment procedures need to be conducted separately. *2
*1 In practice, measurements are conducted multiple times at each point to determine the actual measurement value. Also, the calibration results can only be verified at the points (force value) where the calibrations were conducted. The accuracy of the measurement value when the force between the points is applied is an estimated. The points for conducting calibration should be added as necessary.
*2 The accuracy of measurement values for the individual measuring instrument achieved through adjustment is limited. Please contact the manufacturer for details. In the case of IMADA’s in-house Calibration, the specified accuracy of each measuring instrument is the pass/fail judgment criteria for the calibration results.
Calibration Laboratories for Periodic Calibration
When a new measuring instrument is purchased, the manufacturer performs pre-shipment Calibration (often as a part of the guarantee) in most cases. A calibration provider may be selected from the following two options for the after-purchase periodic Calibration.
- The force gauge manufacturers who have an in-house Calibration facility offering calibration services.
- Calibration Laboratories who specialize in the Calibration of measuring instruments.
When selecting a calibration service provider, consider choosing a provider with appropriate product knowledge, conducting a high level of precision calibration procedures, and the ability to detect abnormal performances.
The manufacturers’ in-house calibration laboratories are also recommended.
The advantages of using the manufacturers’ in-house calibration facilities are that the manufacturer has a high level of product knowledge, can identify problems, and, in the case of repair requirements, has the convenience of catering to smooth and reliable adjustments to follow.
In the case of ISO/IEC 17025 accredited calibrations are required *3, the calibration must be conducted at the accredited calibration laboratories in accordance with ISO/IEC 17025:2017 specifications. (and obtain ISO/IEC 17025 Accredited Calibration Certification).
The manufacturer with the ISO/IEC17025 accredited calibration facilities or laboratories can conduct calibration with the ISO/IEC 17025:2017 specifications, and it is also possible for the manufacturer to perform the pre-shipment ISO/IEC17025 accredited calibration (at cost) upon request.
*3 ISO/IEC17025 Accredited Calibration must be conducted by a calibration facility accredited by an external certification body for calibration with the ISO/IEC 17025:2017 specifications, while General Calibration can beperformed by laboratories without ISO/IEC17025 calibration accreditation. General Calibration performed by the manufacturer is referred to Factory Calibration.
What is ISO/IEC17025 Accredited Calibration?
What does ISO/IEC 17025 accredited calibration mean?This Standard is the single most important international Standard for calibration and testing laboratories worldwide, issued by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
ISO/IEC17025 Accredited Calibration is a Calibration conducted by the Laboratories accredited by an external accreditation provider in accordance with the ISO/IEC 17025:2017 with accredited calibration procedure.
One of the reasons why ISO/IEC17025 accredited calibration is required is the globalization of business. As more and more companies are doing business internationally, calibration results and certificates that are accepted internationally are required. The demand for ISO/IEC17025 accredited calibration is expected to increase in the future due to the reliability of the international standard ISO/IEC17025.
In ISO/IEC17025 accredited calibration, the reliability of the accreditation criteria of accreditation organization, in which each calibration laboratory undergoes an audit, defines the reliability of the calibration results and calibration certificate. So how to find an ISO/IEC17025 accredited calibration laboratories reliable?
“Mutual Recognition Agreement (MRA)” and “International Laboratory Accreditation Cooperation (ILAC-MRA)” help to answer this question.
Mutual Recognition Agreement (MRA)
A Mutual Recognition Agreement (MRA) is a system where accreditation providers evaluate each other’s accreditation criteria and recognize each other as having equivalent criteria for a single standard. This agreement was created to retain a unified accreditation standard across different organizations.
International Laboratory Accreditation Cooperation (ILAC-MRA)
The International Organization for Accreditation, ILAC-MRA is the largest MRA associated with the assessment and accreditation of ISO/IEC17025 calibration laboratories (using ISO/IEC 17025). More than 90 certification bodies participate (as of April 2024) in the ILAC-MRA for mutual recognition.
Calibration laboratories accredited by an ILAC-MRA registered certification body displays the ILAC-MRA symbol on the ISO/IEC17025 accredited calibration certification they issue. The symbol shows the certification is issued by calibration laboratories accredited by an ILAC-MRA registered certification body. Certifications with the symbol are recognized as proof of the calibration result by a calibration laboratory and procedure that have accredited equivalent accreditation standards.
The benefits of using ISO/IEC17025 calibration accredited laboratories with ILAC-MRA registered certification bodies.
- The validity of the ISO/IEC17025 calibration laboratory accreditation that the calibration laboratory has received can be proved.
- Verified certificates with global recognition are issued.
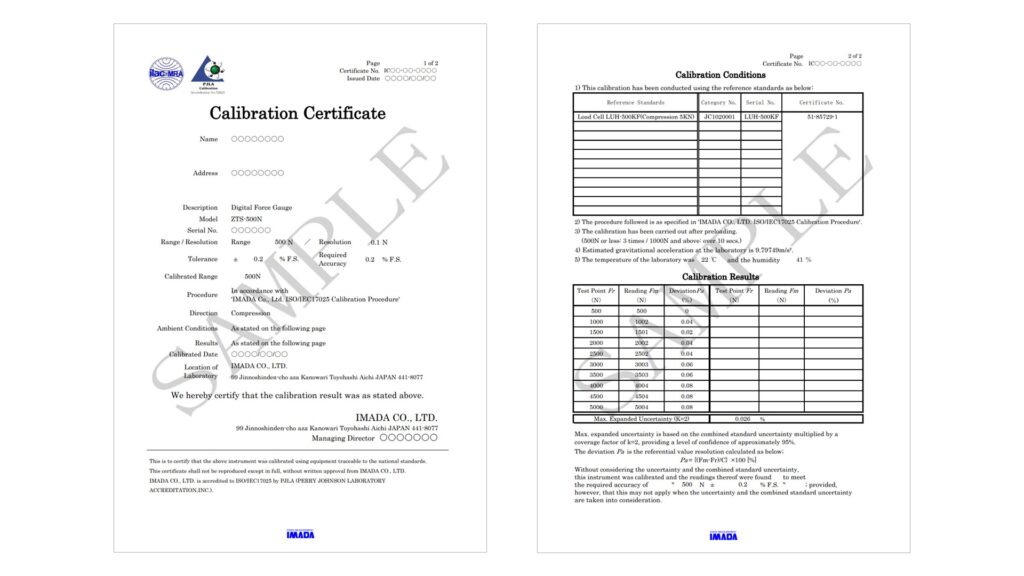
The Certificate displays LAC-MRA and PJLA symbols to certify the accreditation provider.
The indicated values at each calibration point and Max. expanded uncertainty are listed.

Traceability in Calibration
When considering the reliability of calibration results, there is the perspective of whether the values of the standards (weights, etc.) used for calibration are reliable. Even if a calibration laboratory performs calibration according to strict procedures, if the values of the standards are unreliable, the calibration results cannot be trusted either. The reliability of the values of the standards is proved by Traceability.
[Requirements for Calibration Traceability]
- A chain of calibrations: “calibration reference standards are identified” and “The higher standard used to calibrate the standard are identified.” is unbroken and recorded.
- A chain of calibrations can trace back to National Standard.
The necessity of the traceability certification documents is optional and depends on the requirements. However, proof of calibration traceability results is often required by ISO9001 standards, customers, and so on. Verifying the necessary certification documents for each purpose is also essential.
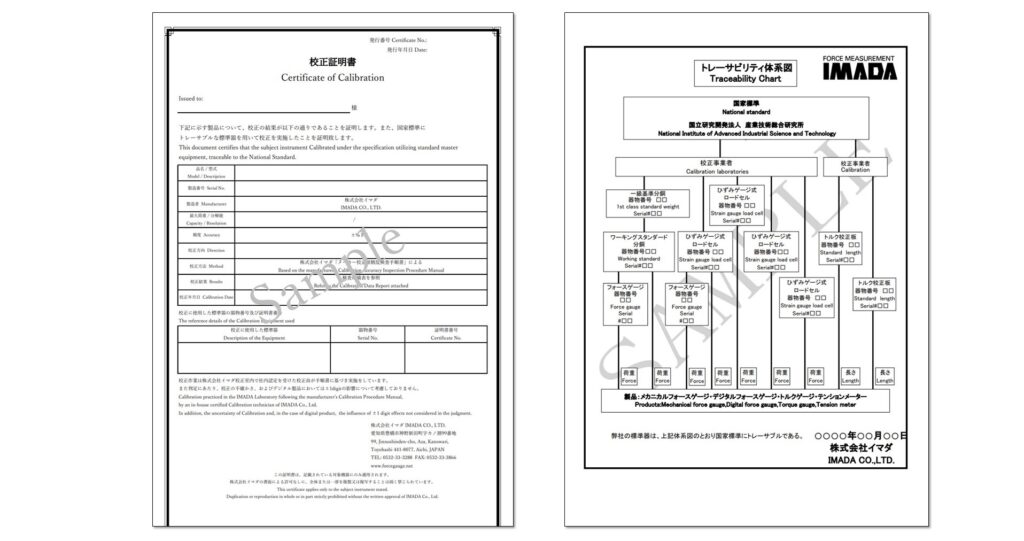
Certification proves that the Standard is traceable to National Standard.
The traceability chart verifies how the calibration standards linked to the National Standard.
The proof of traceability in general and ISO/IEC17025 calibration is provided by the “calibration certificates”. *4 Many calibration laboratories also issue “Traceability Charts” as a complementary document for the reliability of the traceability certification.
*4 Calibration Certificates issued vary depending on the individual Calibration Laboratory. Please check with your calibration laboratory for details.
Conducting Calibration for Different Purposes and Requirements
So far, calibration focused on force measuring instruments have been introduced. For conducting the calibration, the details, such as choosing calibration laboratory, calibration frequency, and certifications, must be based on the clarified purposes.
For instance, the “calibration certificate” and the “traceability chart” for the measuring instrument for in-house use, which will not affect the quality of the product manufactured, may not be necessary. *Company standards and policy should be checked.
On the other hand, obtaining ISO/IEC17025 accredited calibration may be necessary for product quality control. Various requirements must be considered; the standards of your individual customers must be confirmed in addition to the internal product inspection standards. Also, if ISO 9001 certification is required, check the certification criteria, and determine the calibration conducted carefully.
IMADA Co., Ltd. provides ISO/IEC17025 accredited calibrations and factory calibrations in-house for calibration and certification of the IMADA force and torque gauges manufactured. Please feel free to contact our distributor or us with any questions or consultations regarding calibration, measurement value adjustments, and repairs.
Note: The opinions and interpretations expressed in this article are those of IMADA Co., Ltd., and none are certified by Perry Johnson Laboratory Accreditation Inc. (PJLA), the certification body of ISO/IEC17025 calibration for IMADA Co., Ltd.



